In Elderly Patients Analgesic Drugs Tend to
Michael Gloth III MD FACP AGSF Baltimore Maryland Of the community-dwelling elderly population 25-50 can be expected to suffer pain. Several NSAIDs are available without prescription.
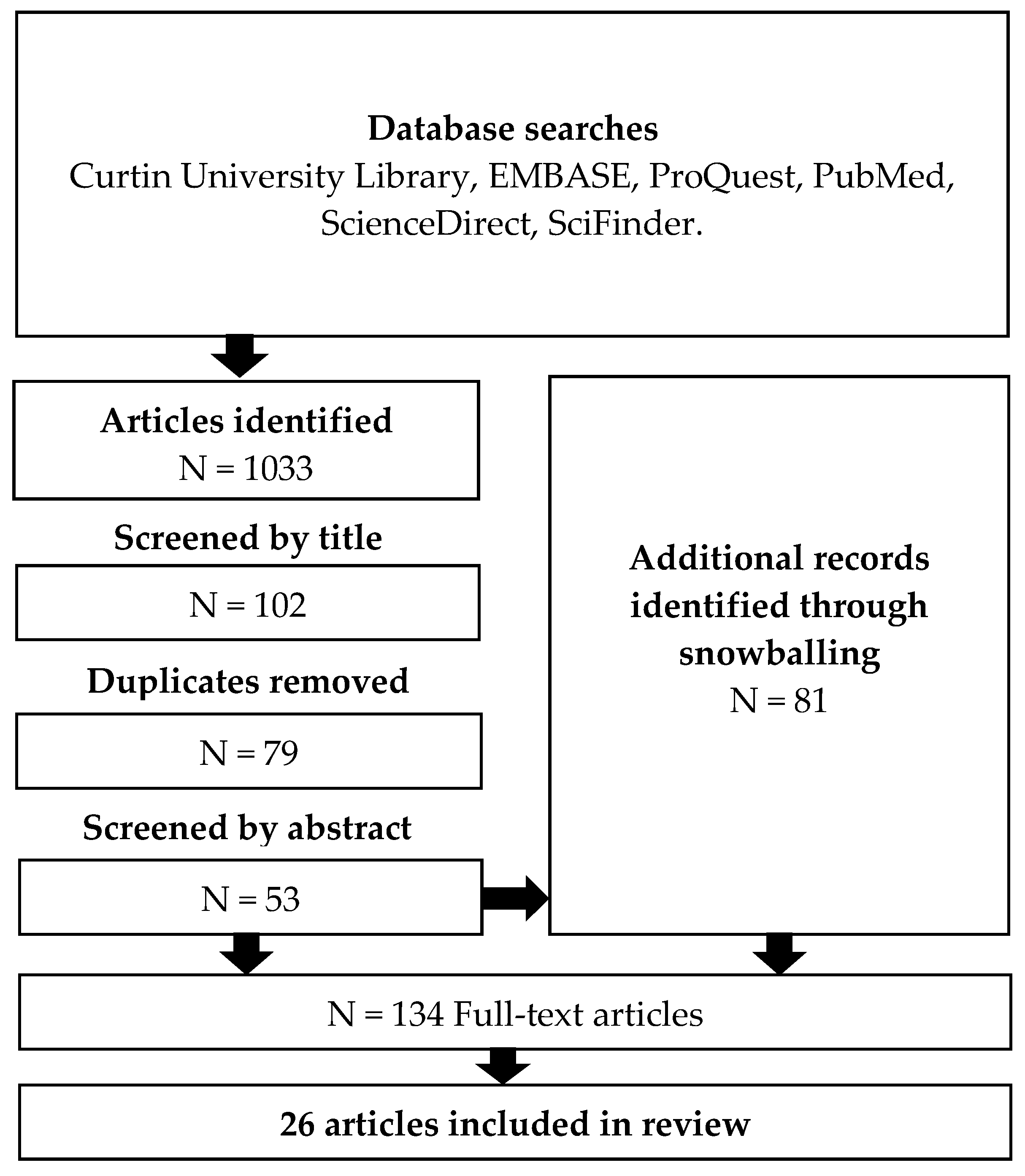
Pharmacy Free Full Text Pain Assessment Of Elderly Patients With Cognitive Impairment In The Emergency Department Implications For Pain Management A Narrative Review Of Current Practices Html
These medicines are used to relieve the pain that arises from migraine headaches.

. Safe and effective use of analgesic medications in geriatric patients requires risk-benefit analysis. Elderly patients who are cognitively impaired tend to have a decreased ability to communicate and report pain which results in the under-detection and under-treatment of pain. To provide optimal analgesic care management of each patient should be individualized.
Rising Opioid Use in Older Adults According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse between 4 and 9 percent of older adults aged 65 and older use prescription opioids to manage their pain. Even if an older patient is capable of properly and consistently managing their medications they may still be overmedicated per their doctors. Tramadol and codeine are opiate based analgesics used for moderate pain both are rather stronger than paracetamol but both can have adverse effects which include constipation increased abdominal pain and nausea.
Percocet 25325 Primlev Roxicet Xartemis XR. Increased Sensitivity to Many Drugs. Unusually high peak of maximum activity Choose the statement that most accurately describes pain reassessment.
Fear of addiction and tolerance are the major barriers to their use among patients as well as health-care professionals. Elderly patients also should be counseled to avoid consuming. Opioid analgesics make the list but by contrast they only accounted for 46 percent of emergency department visits among adults age 65 to 79 and 35 percent among patients age 80 and older.
Overall a total of 10763 92 of all elderly analgesic users were considered to have an inappropriate prescription for the NSAIDs ketorolac or indomethacin although this appeared to be more widespread for ketorolac 9748 patients 84 compared to indomethacin 1237 patients 84 Table 3. As with any patient pay attention to the blood pressure and an alternative agent may be preferable for those with hypotension. The same source reports that opioid prescriptions for older adults increased by a factor of nine.
Drugs to Be Used With Caution in Older Adults Based on the American Geriatrics Society 2019 Beers Criteria Update Analgesics Oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs are used by 30 of people aged 65 to 89 and half of all NSAID prescriptions are for people 60. In contrast the chronic use of non-selective non-steroidal anti. Opioid analgesic drugs in the elderly Much is known about opioid metabolism which is critical in administering these agents to the elderly.
Addressing these issues early in the initiation opioid therapy will help to. The elderly population often receives inadequate pain relief due to 1 ignorance of recommended guidelines for pain control and 2 concern among physicians about prescribing. Propofol is also generally well tolerated in older adults and is the preferred first-line agent in many EDs.
A total of 615 190 of patients experienced pain as defined by a PAINAD-C score of 2. Unusually high peak of maximum activity Symptoms such as weight loss constipation and depression are often seen with. These events are potentially preventable up to 50 percent of the time.
Paracetamol is an effective analgesic particularly for musculoskeletal pain and it is generally well tolerated with few side effects. Chronic pain management in the elderly is complex. Concerns with Chronic Analgesic Therapy in Elderly Patients F.
They may also cause confusion and drowsiness particularly in elderly patients. 7 Many of these ADRs are treated pharmacologically which further increases the number of drugs the patient consumes each day. Adverse drug events occur in 15 percent or more of older patients presenting to offices hospitals and extended care facilities.
Age-related factors affect the safety and efficacy of the analgesic treatment and pharmacological aspects are often underlined especially when impaired cognition and. There are several different classes of drugs that can relieve a migraine such as ergots triptans and NSAIDs. Only 307 95 of patients were treated with analgesic drugs.
It is important that the recommended maximum daily dose does not exceed 4 g24 h. Clinicians are often faced with. The pain of pleurisy is usually treated with analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs such as.
Analgesic Medications and Geriatric Patients. Analgesic medicines also have the potential to provide a burden of potential harm to older people. An analysis of hospital record data for people over 60 years of age in Australia found that analgesics were responsible for approximately 17 of the 37 296 hospital admissions attributed to adverse drug reactions 35.
Some of the risks the elderly may experience when taking opioids are constipation nausea gastrointestinal complications respiratory depression increased falls and sleep disturbances. Unfortunately state-of-the-art analgesic care is not widespread. The treatment of pain-especially chronic pain-with medications can be a demanding task in patients of any age.
Barriers exist in knowledge skills and attitudes among health care providers. Medications in elderly patients. In elderly patients analgesic drugs tend to have.
However applications to pain problems unique to the elderly require greater attention. What type of pain management is used in pleurisy patients. A cohort of persons aged 65 years old with 1 year of database history having at least one analgesic drug NSAIDs strong or weak opioids between.
Patients who develop hepatic andor of NSAIDs in older individuals which may increase their renal dysfunction may need to have their analgesic risk of falls American Geriatrics Society Panel on the dose reduced andor dose administration interval pro- Pharmacological Management of Persistent Pain in longed to reduce side effects and toxicity American Older Persons 2009. The problems of decreased body size altered body composition more fat less water and decreased liver and kidney function cause many drugs to accumulate in older peoples bodies at dangerously higher levels and for longer times than in younger people. These age-related problems are further worsened by the fact that even at.
These changes tend to make older individuals more sensitive to neuraxial and peripheral. In elderly patients analgesic drugs tend to have.

Medical Management Of Acute Pain

Comments
Post a Comment